Hacked Chrome extensions put 2.6 million users at risk of data leakage

Your web browser is an ecosystem of its own. It stores your passwords, search history, credit card numbers, addresses and other financial details. Just like malicious apps and services can compromise data on your phone or PC, malicious extensions can expose data stored in your browser.
There are tons of extensions that do more harm than good. In fact, security researchers have just discovered a dangerous new campaign targeting browser extensions. So far, some 36 extensions have been leaked, putting more than 2.6 million Chrome users at risk of exposing their browsing profiles and account credentials.
I’m giving away the latest and greatest AIRPODS PRO 2
Sign up for my account to get freebies Free newsletter.
People using Chrome browser extensions (Kurt “CyberGuy” Knutson)
How hackers target browser extensions
Hackers are using browser extensions as gateways to steal sensitive user information through various methods. These compromised extensions reportedly put more than 2.6 million users at risk of data exfiltration and credential theft Hacker News.
Common attacks involve phishing campaigns targeting legitimate extension publishers on platforms such as the Chrome Web Store. In these campaigns, attackers trick developers into granting permissions to malicious applications and then insert harmful code into popular extensions. This code can steal cookies, access tokens, and other user data.
The first company to disclose the campaign was cybersecurity company Cyberhaven, where an employee was targeted in a phishing attack on December 24, leading the threat actor to release a malicious version of the extension. .
Once these malicious extensions are released and pass the Chrome Web Store’s security review, they are made available to millions of users, putting them at risk of having their data stolen. Attackers can use these extensions to steal browsing data, monitor user activity, and even bypass security measures such as two-factor authentication.
In some cases, developers themselves may unknowingly include data collection code as part of a monetization software development kit, secretly leaking detailed browsing data. This makes it difficult to determine whether the compromise is the result of hacker activity or intentional inclusion by the developers.

Image of Chrome browser on mobile phone (Kurt “CyberGuy” Knutson)
Massive security flaw on Mac puts most popular browser at risk
Remove these extensions from your web browser
Browser extension security platform safety accessories has launched its own investigation into the hack. So far, it has discovered more than two dozen additional compromised extensions, listed below. If any of the infected extensions listed in the Secure Annex investigation are installed on your browser, you must delete them immediately to protect your data.
- AI Assistant – ChatGPT and Gemini Chrome Edition
- Bard AI Chat Extension
- OpenAI’s GPT 4 Summary
- Search Copilot AI Assistant for Chrome
- TinaMINd Artificial Intelligence Assistant
- Weiyin Artificial Intelligence
- vpn city
- Internet VPN
- Vindoz Flex Video Recorder
- VidHelper video downloader
- Bookmark icon changer
- Nutria
- Excellent voice
- reader mode
- parrot speech
- Primus
- Tapker – Online keylogging tool
- Artificial Intelligence Shop Friends
- Sort by oldest
- Reward Search Automator
- ChatGPT Assistant-Intelligent Search
- Keyboard history recorder
- email hunter
- Google Meet visuals
- Earny – up to 20% cash back
- Cyberhaven Security Extensions V3
- GraphQL Network Inspector
- Vidnoz Flex – Video recorder and video sharing
- Yes verification code assistant
- Agent SwitchyOmega (V3)
- Chat GPT App
- Network mirroring
- Hi Ai
Leaving these extensions installed is a serious risk because hackers can still access your data even if the malicious version has been removed from the Chrome Web Store. Secure Annex is still investigating and shared Public Google Sheets Contains details about malicious extensions discovered so far, such as whether they have been updated or removed. They’ll also add new extensions to the list as they discover them.
The world’s largest database of stolen passwords has been uploaded to a criminal forum
How to remove extensions from Google Chrome
If you have one of the above extensions installed on your browser, please remove it as soon as possible. To remove extensions from Google Chrome, follow these steps:
- Open Chrome and click Icon that looks like a puzzle piece. You can find it in the upper right corner of your browser.
- Now you can see all active extensions. Click three dot icon Next to the extension you want to delete, then select Remove from Chrome.
- Click eliminate confirm
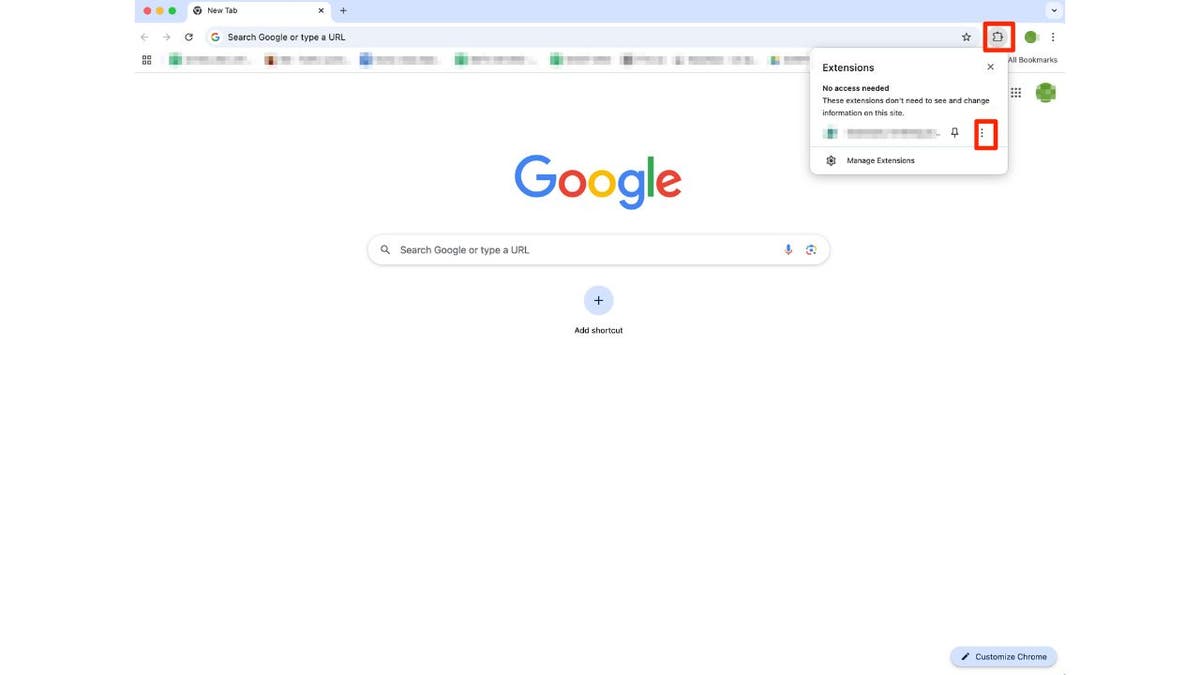
Steps to remove extensions from Google Chrome (Kurt “CyberGuy” Knutson)
THE BEST ANTIVIRUS SOFTWARE FOR MAC, PC, IPHONE & Android – CYBERGUY’S PICKS
7 ways to avoid malware
1) Verify email and link before clicking: Many attacks start with Phishing e-mail Impersonating a trusted entity, such as Google Chrome Web Store Developer Support. These emails often create a false sense of urgency, urging you to click on a malicious link. Be sure to verify the sender’s email address and avoid clicking on links without double-checking their authenticity. If in doubt, please visit the official website directly instead of using the link provided.
2) Use powerful anti-virus software: Having strong antivirus software is an important line of defense against malware. These tools can detect and block malicious code even if it’s embedded in a browser extension. The best way to protect yourself from malicious links that install powerful malware and potentially access your private information is to install antivirus software on all your devices. This protection also alerts you to phishing emails and ransomware scams, keeping your personal information and digital assets safe. Get my picks for the 2025 winners of the best antivirus protection for your Windows, Mac, Android, and iOS devices.
3) Limit expansion permissions: Please be careful about the permissions you grant to browser extensions. Many requests require access to sensitive data such as browsing history, cookies, or account information, but not all requests are necessary. Review the content of each extension request and deny permissions that appear to be excessive. If possible, choose an extension with limited access to ensure your data is protected.
4) Limit the number of extensions: Only install extensions you really need, and regularly check and uninstall extensions you no longer use.
5) Keep your browser updated: Always update your browser to the latest version. Updates often include important security patches that prevent malware from exploiting vulnerabilities. Using an outdated browser increases the risk of attacks that could be prevented with simple updates. Enable automatic updates to ensure you’re always protected. If you’re not sure how to update your browser, check out my A detailed guide to Google Chrome.
6) Review your extensions regularly: Perform regular checks on installed extensions and remove any extensions that are unnecessary or pose a potential security risk.
7) Report suspicious extensions: If you come across a suspicious extension, please report it to the official browser extension marketplace.
Subscribe to KURT’s YouTube channel for quick video tips on how to use all your tech devices
Kurt’s key takeaways
Hackers are getting smarter, and browser extensions have become a new favorite target for stealing sensitive data. The discovery of more than 35 infected Chrome extensions, putting 2.6 million users at risk, is a wake-up call for everyone. Removing suspicious extensions is an important step in protecting your data. It also puts Google’s Chrome Web Store review process under intense scrutiny, proving that even a trusted platform can be exploited.
How often do you check for and remove unused or suspicious browser extensions? Please write to us Cyberguy.com/contact.
For more of my tech tips and security alerts, subscribe to my free CyberGuy Reports newsletter by going to Cyberguy.com/Newsletter.
Ask Kurt a question or let us know what stories you’d like us to cover.
Follow Kurt on his social channels:
Answers to CyberGuy’s most frequently asked questions:
New news from Kurt:
Copyright 2024 CyberGuy.com. all rights reserved.


